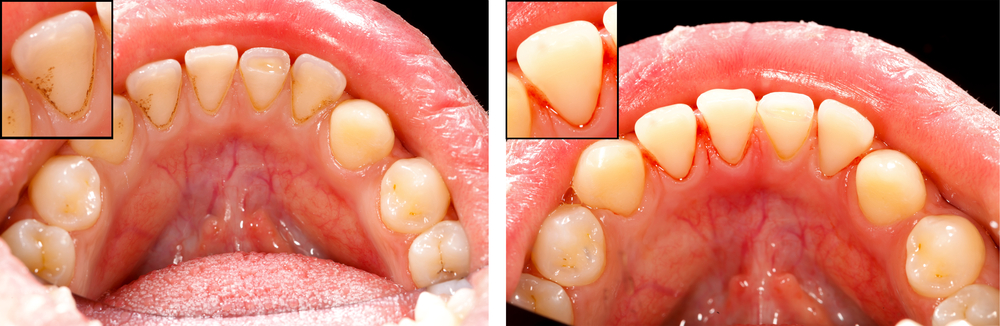
The Early Signs of Gum Disease You Shouldn’t Ignore
Have you ever wondered if there are early signs of gum disease that you might be overlooking? Well, the truth is, gum disease can often go unnoticed until it reaches a more advanced stage.
However, there are some subtle indications that you shouldn’t ignore. From red or swollen gums to bleeding during brushing or flossing, these signs may seem insignificant at first, but they could be early warning signals of a larger problem.
But that’s not all there are a few more signs that you need to be aware of. So, keep on reading to discover the early signs of gum disease that you might not be paying enough attention to.
Red or Swollen Gums
If you notice that your gums are red or swollen, it may be an early sign of gum disease. Red or swollen gums can indicate inflammation caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth. When plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria, isn’t properly removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can irritate and infect your gums. This can lead to gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease.
Gingivitis is characterized by redness, swelling, and tenderness in the gums. You may also notice that your gums bleed easily, especially when you brush or floss. These signs shouldn’t be ignored, as untreated gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of gum disease, such as periodontitis.
To prevent gum disease, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene. Make sure to brush your teeth at least twice a day, using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque between your teeth and along the gumline. Additionally, regular visits to your dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups are essential.
If you notice any signs of red or swollen gums, it’s crucial to seek dental care promptly. Your dentist can evaluate your oral health, provide appropriate treatment, and give you advice on how to prevent gum disease in the future. Remember, early detection and intervention can help maintain your oral health and prevent further complications.
Bleeding During Brushing or Flossing
When you notice bleeding during brushing or flossing, it’s a possible indication of early gum disease. Bleeding gums can occur due to the buildup of plaque and bacteria along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film that forms on your teeth and contains harmful bacteria. If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, which irritates the gums and leads to inflammation.
When your gums bleed, it’s a sign that they’re inflamed and more susceptible to infection. This condition is known as gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease. Gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral hygiene practices and regular dental cleanings. However, if left untreated, it can progress to a more severe form of gum disease called periodontitis, which can cause irreversible damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
To address bleeding gums, make sure you’re brushing your teeth gently using a soft-bristled brush. Avoid aggressive brushing, as it can further irritate the gums. Additionally, incorporate daily flossing into your oral care routine to remove plaque and bacteria from between the teeth.
If your gums continue to bleed despite proper oral hygiene, it’s important to schedule an appointment with your dentist. They can evaluate the health of your gums, provide necessary treatment, and offer guidance on maintaining optimal oral hygiene. Remember, addressing bleeding gums early can help prevent the progression of gum disease and maintain a healthy smile.
Receding Gumline
To address receding gumline, it’s important to be aware of the factors that can contribute to this condition. Receding gumline occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth starts to pull back, exposing more of the tooth and its root.
One of the main causes of this condition is poor oral hygiene. Not brushing and flossing regularly can lead to the buildup of plaque and tartar, which can irritate and inflame the gums, causing them to recede.
Another factor is aggressive brushing. Brushing too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can wear away the gum tissue, leading to gum recession.
Grinding or clenching your teeth can also contribute to receding gumline. The excessive force exerted during these habits can put pressure on the gums and cause them to recede over time.
Additionally, genetics, hormonal changes, smoking, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of developing receding gumline.
If you notice your gums pulling back or your teeth appearing longer, it’s important to see a dentist for evaluation and treatment. Early detection and intervention are key in preventing further gum recession and potential tooth loss.
Persistent Bad Breath
One common consequence of receding gumline is persistent bad breath, which can be caused by a buildup of bacteria in the gaps between the teeth and gums. When bacteria accumulate in these spaces, they release foul-smelling gases that result in chronic halitosis. If you’ve noticed that your breath has a consistently unpleasant odor, it could be an early sign of gum disease.
Here are some important points to consider:
– Causes of persistent bad breath:
– Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which harbors bacteria and causes bad breath.
– Gum infection: When the gums recede, it creates pockets where bacteria can thrive, causing an infection and contributing to bad breath.
– Other symptoms to look out for:
– Red, swollen, or bleeding gums: These are signs of gum inflammation, which can worsen bad breath.
– Loose teeth: Receding gums can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
If you’re experiencing persistent bad breath, it’s crucial to address the underlying cause. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can help prevent gum disease and maintain fresh breath. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene is essential for overall oral health and fresh breath.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
If you’ve noticed your teeth becoming loose or shifting in your mouth, it may be a sign of gum disease. When your gums are healthy, they provide support and stability to your teeth. However, if gum disease sets in, it can weaken the tissues that hold your teeth in place. This can result in teeth that feel loose or start to shift position.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is caused by bacteria that build up in the mouth. These bacteria can lead to inflammation and infection of the gums, which can eventually damage the supporting structures of the teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can progress and lead to tooth loss.
There are several reasons why gum disease can cause teeth to become loose or shift. Firstly, the bacteria can attack the gum tissue and bone that support the teeth, causing them to weaken. Secondly, as the gums become inflamed, they can pull away from the teeth, creating pockets where bacteria can thrive. This further exacerbates the damage to the supporting structures of the teeth.
If you notice any changes in the position or stability of your teeth, it’s essential to visit a dentist as soon as possible. They can evaluate the health of your gums and provide appropriate treatment to prevent further damage. Remember, early detection and intervention are crucial in managing gum disease and preserving your oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Gum Disease Be Reversed or Cured Completely?
Yes, gum disease can be reversed or cured completely with proper treatment and oral hygiene habits. Regular brushing and flossing, along with professional cleanings by a dentist or dental hygienist, can help remove plaque and tartar buildup, which are the main causes of gum disease.
In more advanced cases, additional treatments like scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, or surgery may be necessary. It’s important to address gum disease early to prevent further damage to your gums and teeth.
What Are Some Common Risk Factors for Developing Gum Disease?
Some common risk factors for developing gum disease include:
– Poor oral hygiene
– Smoking or tobacco use
– A family history of gum disease
– Hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy or menopause)
– Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
– Certain health conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders
Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and avoiding tobacco use can help reduce your risk of developing gum disease.
Are There Any Natural Remedies or Home Treatments for Gum Disease?
There are several natural remedies and home treatments that can help alleviate gum disease.
One option is to regularly rinse your mouth with a saltwater solution, as this can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria.
Another option is to apply aloe vera gel to your gums, as it has anti-inflammatory properties.
Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly, can play a crucial role in preventing and treating gum disease.
How Often Should I Visit a Dentist for Check-Ups and Cleanings to Prevent Gum Disease?
You should visit a dentist for check-ups and cleanings regularly to prevent gum disease. The frequency of these visits depends on your individual dental needs and the recommendations of your dentist.
Typically, it’s recommended to have a dental check-up and cleaning every six months. However, some individuals with certain risk factors may need more frequent visits. Your dentist will be able to assess your oral health and provide guidance on how often you should schedule these appointments.
Can Gum Disease Lead to Other Health Problems or Complications?
Gum disease can indeed lead to other health problems or complications. It’s not just about tooth and gum issues, but it can also affect your overall health. If left untreated, gum disease has been linked to conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
The bacteria in your mouth can travel through your bloodstream and cause inflammation in other parts of your body. So, it’s important not to ignore the early signs of gum disease and to seek treatment from a dentist.
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s important not to ignore the early signs of gum disease. Red or swollen gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing, receding gumline, persistent bad breath, and loose or shifting teeth are all indicators that shouldn’t be overlooked.
Taking prompt action and seeking den look at this web-site tal care can help prevent further damage and maintain good oral health. Don’t ignore these signs; prioritize your gum health for a brighter smile.

Welcome to my website! My name is Jacob Wearne, and I am thrilled to be your guide in the world of orthodontic innovations, pediatric dental care, cosmetic smile solutions, and dental technology trends. As a professional Orthodontic Innovations Specialist, I am passionate about transforming smiles and improving oral health for patients of all ages.