Introduction
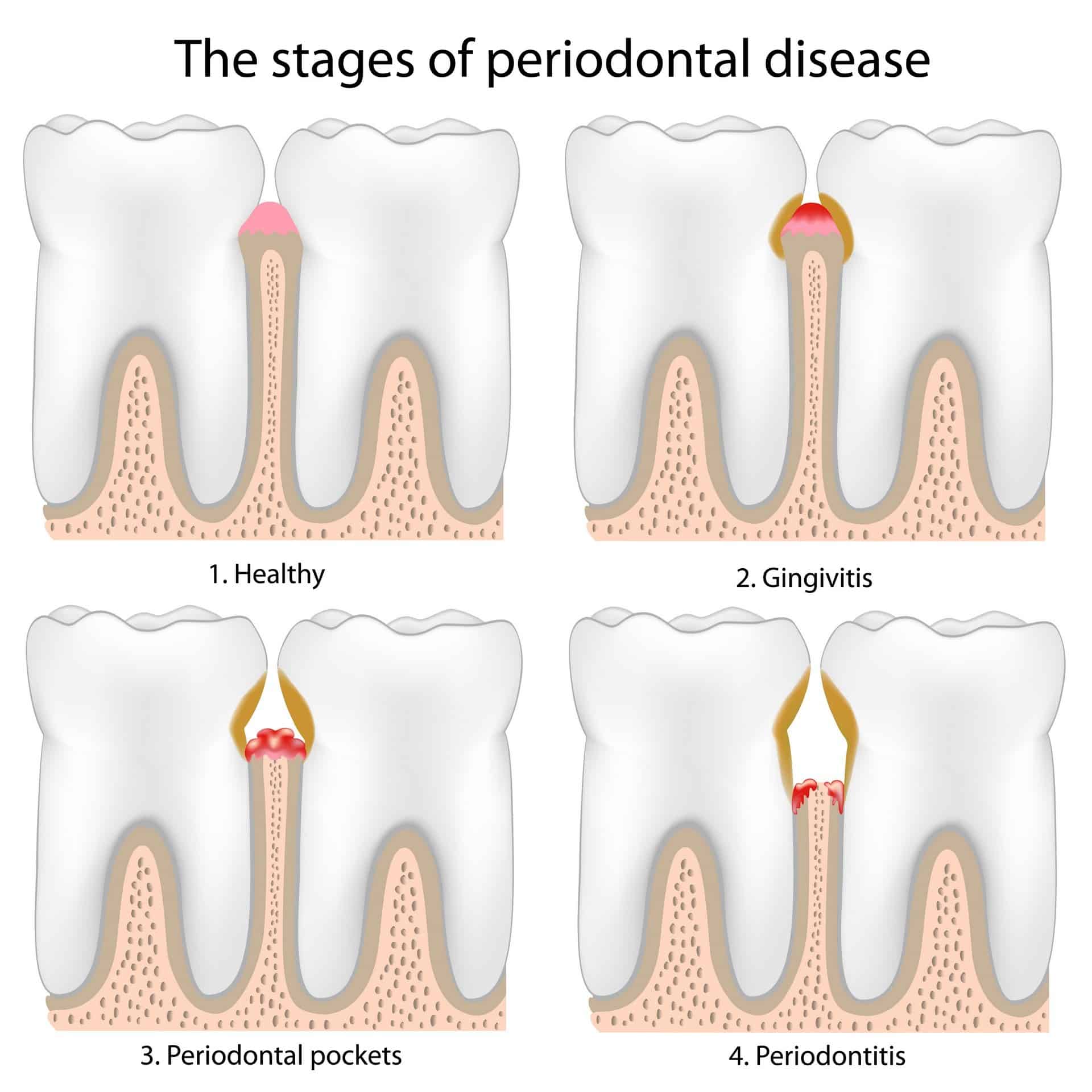
Gingivitis and periodontitis are common oral health conditions that affect the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can lead to tooth loss. Fortunately, periodontal therapy offers effective treatment options to manage and control these conditions, preventing further damage to the oral tissues.
Understanding Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis and periodontitis are two common gum diseases that affect millions of people worldwide. Gingivitis is the milder form of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe condition that can lead to tooth loss. Both conditions require proper periodontal therapy to prevent further damage and restore oral health.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gingivitis and periodontitis is crucial for early detection and treatment. Common symptoms include:
Gingivitis:
- Red, swollen, and tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially during brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
- Receding gumline
Periodontitis:
- Persistent bad breath
- Gum recession
- Pockets forming between teeth and gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain or discomfort while chewing
Periodontal Therapy Options
Periodontal therapy aims to control the progression of gum disease, eliminate infection, and restore gum health. Here are some common treatment options:
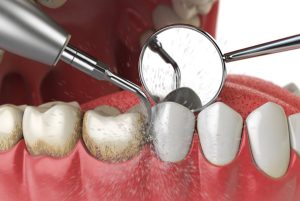
Scaling and Root Planing
This non-surgical procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surfaces and smoothing the root surfaces to prevent bacteria buildup. It helps reduce inflammation and promotes gum healing.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infection. They can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to remove infected tissue and promote gum regeneration. It is effective in reducing pocket depth and improving overall gum health.
Summary
Periodontal therapy plays a crucial role in the management of gingivitis and periodontitis. It involves various treatment approaches aimed at reducing inflammation, controlling infection, and promoting gum tissue healing. The primary goal of periodontal therapy is to restore and maintain the health of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. This can be achieved through professional dental cleanings, scaling and root planing, antibiotic therapy, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Regular dental visits and proper oral hygiene practices are essential for the long-term success of periodontal therapy. By seeking timely treatment and adopting good oral care habits, individuals can effectively manage gingivitis and periodontitis, preserving their oral health view it now and overall well-being.
- Q: What is periodontal therapy?
- A: Periodontal therapy refers to the treatment of gum diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Q: What is gingivitis?
- A: Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by plaque buildup. It is the earliest stage of gum disease.
- Q: What is periodontitis?
- A: Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease where the infection has spread to the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone.
- Q: How is gingivitis treated?
- A: Gingivitis can be treated through professional dental cleanings, improved oral hygiene practices, and regular check-ups with a dentist.
- Q: How is periodontitis treated?
- A: Periodontitis may require more extensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing, gum surgery, or antibiotic therapy, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Q: Can periodontal therapy reverse gum disease?
- A: While periodontal therapy can help manage and control gum disease, it may not be able to fully reverse the damage caused by advanced periodontitis.
- Q: How can I prevent gum disease?
- A: Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings, can help prevent gum disease. Avoiding tobacco use and eating a balanced diet also contribute to gum health.
- Q: Is periodontal therapy painful?
- A: Periodontal therapy can cause some discomfort during and after the treatment, but local anesthesia and pain management techniques are used to minimize any pain or discomfort.