The Role of Pollution in Environmental Health Risks
Did you know that pollution plays a significant role in environmental health risks? It’s true!
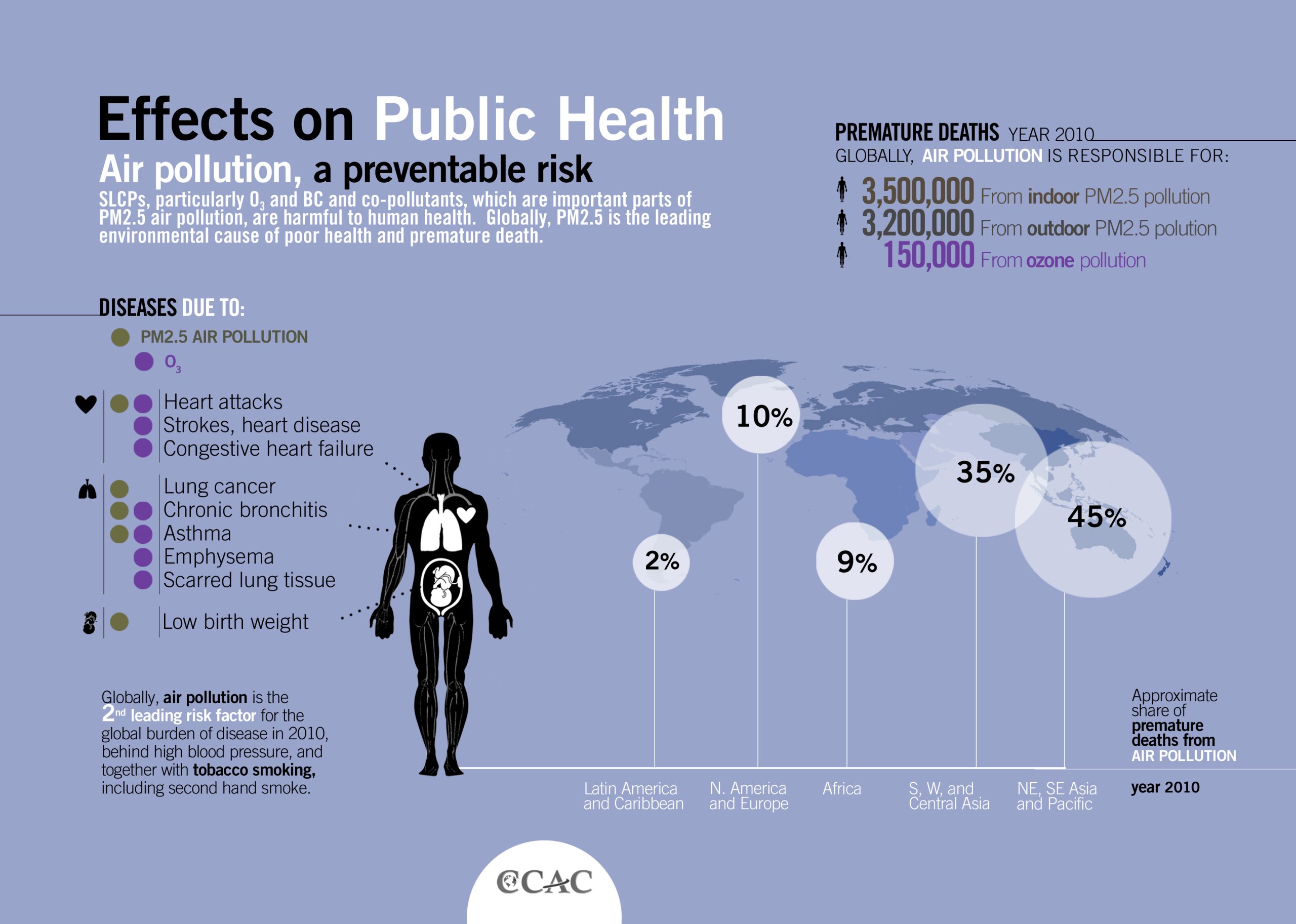
In fact, according to a recent study, pollution is responsible for a staggering 9 million premature deaths worldwide each year. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need to understand the impact of pollution on our health and take steps to mitigate its harmful effects.
From air pollution caused by emissions from industries and vehicles to water and soil pollution from improper waste disposal, pollution affects every aspect of our environment.
In this article, we will explore the different types of pollution, their sources, and the consequences they have on our health.
So, let’s delve into the role of pollution in environmental health risks and discover ways to protect ourselves and our planet.
Key Takeaways
– Pollution, including air, water, soil, noise, and light pollution, has significant impacts on both human health and the environment.
– Industrial processes, transportation, and agricultural practices are major sources of pollution.
– Air pollution can lead to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and an increased risk of cancer.
– Water pollution can cause gastrointestinal issues, damage to liver and kidneys, and harm aquatic ecosystems, leading to economic implications and clean-up efforts.
Types of Pollution
To understand the various ways pollution affects environmental health risks, you need to be familiar with the different types of pollution. Pollution comes in many forms, each with its own detrimental effects on the environment and human health.
One of the most common types of pollution is air pollution, which occurs when harmful substances are released into the atmosphere. This can be caused by industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and the burning of fossil fuels. Breathing in polluted air can lead to respiratory problems, such as asthma and lung cancer.
Water pollution is another significant form of pollution that poses serious threats to both the environment and human health. It occurs when contaminants, such as chemicals and waste, enter bodies of water, making them unsafe for consumption and recreation. Drinking contaminated water can result in waterborne diseases, including cholera and dysentery.
Additionally, soil pollution is a major concern as it affects the quality of the land and can contaminate crops and groundwater. This type of pollution is often caused by the improper disposal of hazardous waste and the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers. Ingesting food grown on polluted soil can lead to various health issues, such as neurological disorders and cancer.
Sources of Pollution
You can identify the sources of pollution by examining the various human activities that contribute to environmental degradation. Pollution can originate from both point sources and non-point sources.
Point sources include factories, power plants, and wastewater treatment plants, where pollution is released from a single identifiable location. These sources often release large quantities of pollutants, such as chemicals, heavy metals, and gases, directly into the environment.
Non-point sources, on the other hand, are more diffuse and include activities like agriculture, urban runoff, and transportation. These sources contribute to pollution through the release of contaminants into the air, water, and soil, often as a result of everyday activities.
Industrial processes are significant contributors to pollution, with emissions from factories and power plants being major sources of air pollution. These emissions include greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, as well as pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Transportation, particularly the burning of fossil fuels in vehicles, also releases significant amounts of air pollutants. In addition, agricultural practices, such as the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, contribute to water pollution through runoff, which can contaminate rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
Understanding the sources of pollution is crucial for implementing effective pollution control measures. By identifying and addressing these sources, we can work towards reducing pollution and mitigating its harmful effects on our environment and health.
Impact of Air Pollution
The impact of air pollution on environmental health risks can be seen through the emissions released from point sources and non-point sources, contributing to the contamination of the air we breathe. Air pollution is a major concern worldwide, as it not only affects the environment but also poses significant health risks to humans and other living organisms.
One of the main ways in which air pollution impacts our health is through the release of harmful pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. These pollutants can have detrimental effects on our respiratory system, leading to the development or exacerbation of respiratory diseases like asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Additionally, air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. The fine particles present in polluted air can enter our bloodstream and cause inflammation, leading to the formation of plaque in our arteries and the narrowing of blood vessels.
Furthermore, long-term exposure to air pollution has been associated with an increased risk of cancer, particularly lung cancer. The carcinogenic substances present in polluted air, such as benzene and formaldehyde, can damage our DNA and increase the likelihood of cancer development.
Consequences of Water Pollution
Water pollution has serious consequences that can directly impact your health and the environment.
Contaminated water sources can lead to a wide range of health problems. Drinking water that’s contaminated with harmful chemicals or bacteria can cause gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea and vomiting. It can also lead to long-term health effects, including liver and kidney damage, as well as an increased risk of cancer.
In addition to the direct impact on human health, water pollution also has severe consequences for the environment. Aquatic ecosystems can be greatly affected by the presence of pollutants in the water. Chemicals and toxins can harm fish and other aquatic organisms, leading to declines in population and even extinction. Additionally, the pollution can disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem, affecting the entire food chain.
Water pollution can also have economic implications. Contaminated water sources can render water unfit for irrigation or industrial use, leading to decreased agricultural productivity and increased costs for industries that rely on clean water. Furthermore, the clean-up and restoration efforts required to address water pollution can be financially burdensome.
Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human health. When soil becomes contaminated with pollutants, it can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems and harm the organisms that rely on it for survival. One of the immediate effects of soil pollution is the loss of biodiversity. Pollutants can kill or inhibit the growth of certain plant and animal species, leading to a decrease in overall species diversity. This can disrupt food chains and ecological processes, ultimately impacting the stability of ecosystems.
Additionally, soil pollution can have direct consequences on human health. Contaminated soil can contaminate crops, leading to the ingestion of harmful substances through the food chain. This can result in various health problems, ranging from mild symptoms like nausea and vomiting to more serious conditions like organ damage and cancer. Moreover, pollutants in soil can also seep into groundwater, contaminating drinking water sources and posing a risk to human health.
It is important to address soil pollution through various measures, such as proper waste management, implementing sustainable agricultural practices, and promoting the use of organic fertilizers. By taking action to prevent and mitigate soil pollution, we can protect both the environment and human health from its detrimental effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Pollution on Human Health?
The long-term effects of pollution on your health can be significant. Air pollution, for example, can lead to respiratory problems such as asthma and lung cancer.
Water pollution can expose you to harmful contaminants that may cause gastrointestinal issues and even certain types of cancer.
Additionally, exposure to pollution can weaken your immune system and increase the risk of developing chronic illnesses.
It’s important to prioritize environmental protection to mitigate these health risks.
How Does Pollution Contribute to Climate Change?
Pollution contributes to climate change by releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. When you burn fossil fuels for energy or drive cars that emit exhaust, you release carbon dioxide, methane, and other gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. These gases then contribute to the greenhouse effect, causing the Earth’s temperature to rise.
This rise in temperature leads to a range of environmental and health risks, including extreme weather events, sea-level rise, and the spread of diseases.
Are There Any Natural Sources of Pollution?
Yes, there are natural sources of pollution.
For example, volcanic eruptions release gases and particles into the atmosphere, which can have harmful effects on air quality.
Forest fires also emit pollutants such as smoke and ash.
Additionally, dust storms and pollen from plants can contribute to air pollution.
While human activities are a major contributor to pollution, it’s important to recognize that nature itself can also be a source of pollution.
What Are the Economic Costs of Pollution on Society?
The economic costs of pollution on society can be significant. Pollution can lead to increased healthcare expenses, as people become sick from exposure to pollutants. It can also harm industries, such as agriculture and tourism, which rely on clean environments.
Additionally, pollution can damage infrastructure, leading to costly repairs. Moreover, it can negatively impact property values and decrease overall economic productivity.
Therefore, addressing pollution is crucial for minimizing its economic burdens on society.
How Can Individuals Reduce Their Exposure to Pollution in Their Daily Lives?
To reduce your exposure to pollution in your daily life, there are several steps you can take.
First, try to limit your time spent in areas with heavy pollution, such as busy roads.
Second, make sure to properly ventilate your home to reduce indoor air pollution.
Third, use public transportation or carpool whenever possible to reduce emissions.
Finally, support and advocate for policies that aim to reduce pollution and promote clean energy sources.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pollution plays a significant role in environmental health risks.
The various types of pollution, such as air, water, and soil pollution, have detrimental effects on the environment and human health.
It’s crucial to address the sources of pollution and take necessary measures to reduce imp source its impact.
By actively working towards minimizing pollution, we can create a healthier and sustainable environment for future generations.

Welcome to my website! My name is Liam Lymburner, and I am a dedicated professional in the field of sanitation. With years of experience as a Sanitation Specialist, I have developed a deep understanding of advanced cleaning technologies, commercial cleaning services, sustainable practices, and hygiene education.